Clogged & blocked ears: symptoms, causes and treatments

Clogged & blocked ears: symptoms, causes and treatments
5 minutes
Lifestyle 4 September 2025
Lifestyle 4 September 2025
Blocked ears are a common problem that many people experience at some point. While it's often a temporary issue, the feeling of fullness in your ears can be uncomfortable and affect your daily routine. Whether it's caused by earwax buildup, an infection, or changes in pressure, understanding the causes and treatments of blocked ears will help you feel better.
This issue affects millions of people around the world, and it can range from mild irritation to more serious concerns like hearing loss or infections. Spotting the symptoms early and knowing what to do can help prevent things from getting worse and keep your hearing healthy.
Understanding blocked ears
Blocked ears happen when something interferes with the normal function of your ear. To understand this better, it's useful to know how the ear is structured and how it works.
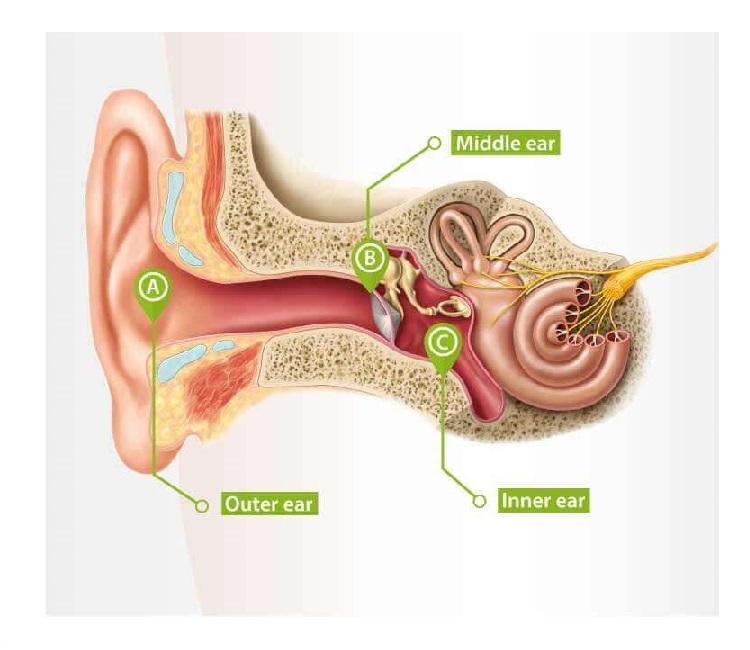
Anatomy of the ear
The ear is made up of three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
Outer ear: this is the visible part of your ear (the pinna) and the ear canal. It collects sound waves and directs them to the eardrum.
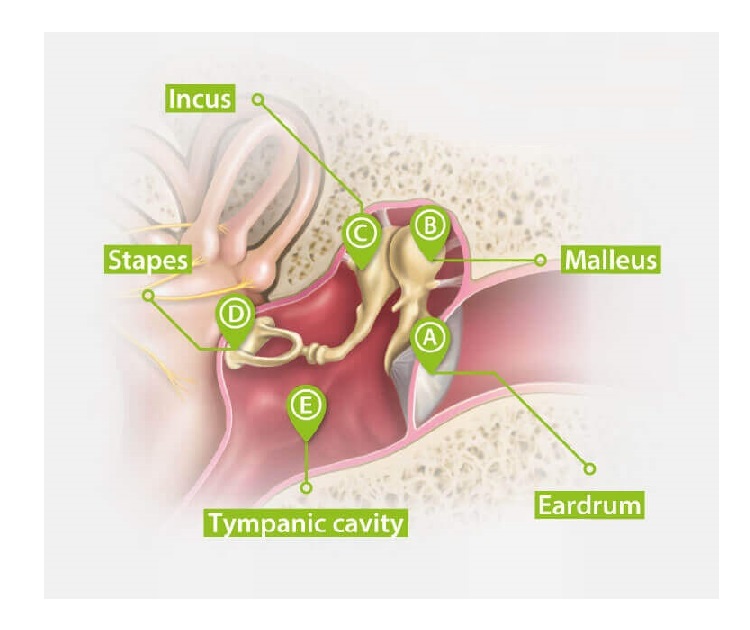
Middle ear: it contains the eardrum and three tiny bones that amplify sound and send vibrations to the inner ear.
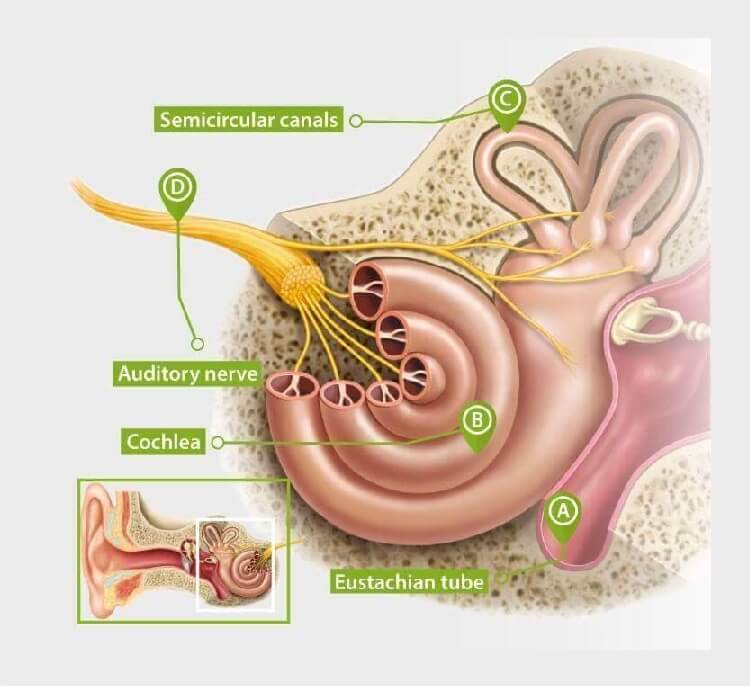
Inner ear: the cochlea converts sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain understands as sound. The inner ear also helps with balance.
The Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of your nose and throat, helps balance pressure in the ear. If this tube gets blocked or doesn't work properly, it can lead to the feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears.
What does it mean when your ears feel blocked?
Blocked ears often feel full, pressurised, or muffled. You might also have trouble hearing clearly or feel discomfort or pain. The sensation can affect one or both ears.
There are two main types of ear blockage:
Temporary blockage: this is often caused by things like earwax buildup, pressure changes (like flying or diving), or a cold. Temporary blockages usually go away on their own or with simple treatments like swallowing or using ear drops. If you have blocked ears from the cold, read our guide for more information.
Persistent blockage: if the feeling lasts a long time, or if you have pain, drainage, or hearing loss, it may be a more serious problem, like an ear infection. In this case, it's important to see a healthcare professional.
Why are my ears blocked?
There are several reasons your ears might feel blocked. The most common cause is earwax buildup, but other factors can also contribute to the problem.
Earwax build-up
Earwax is a natural substance that helps protect your ears by trapping dust, dirt, and bacteria. However, too much wax or impacted wax can cause a blockage and make the ear feel full.
Here's why earwax might build up:
• More wax production: some people naturally produce more earwax.
• Use of earplugs or hearing aids: regular use can push earwax deeper into the ear.
• Improper cleaning: using cotton swabs or other objects can push earwax further in, making it harder to remove.
• Age: as people get older, earwax becomes drier and harder to remove.
If earwax is causing your blockage, try ear drops or see a professional for safe earwax removal, never use cotton swabs.
Eustachian tube dysfunction
The Eustachian tube regulates pressure between the middle ear and the outside world. When it becomes blocked or doesn't work properly, it can lead to a feeling of fullness in the ears. This is known as Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD). Causes include:
• Colds and allergies: these can cause swelling in the nasal passages, which may block the Eustachian tube, leading to a feeling of fullness in the ear.
• Infections: both viral and bacterial infections can cause inflammation and congestion, obstructing the Eustachian tube and making it difficult for the ear to regulate pressure.
• Altitude changes: activities like flying or diving can create pressure differences that the Eustachian tube may struggle to balance, resulting in blocked or "popping" ears.
Middle Ear Infections (Otitis Media)
Middle ear infections are a common cause of blocked ears, especially in children. These infections occur when the middle ear becomes inflamed, often due to a cold or infection. The inflammation can lead to fluid buildup, causing discomfort and the feeling of blocked ears.
Causes of middle ear infections include:
• Colds and respiratory infections: these can cause swelling in the Eustachian tube, leading to fluid buildup in the middle ear.
• Bacterial or viral infections: these infections can directly affect the middle ear, causing pain, swelling, and fluid (pus).
• Allergies: allergies can also contribute to inflammation and fluid buildup, increasing the risk of infection.
Symptoms of middle ear infections
When your ears are blocked, the symptoms are usually related to your hearing and comfort. Here are some common signs:
• Ear pain or discomfort
• Hearing loss or muffled hearing
• Fluid drainage from the ear (in more severe cases)
• A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
How infections lead to fluid buildup and blockage
When the middle ear is infected, your body produces fluid as part of the immune response. This fluid can accumulate behind the eardrum, causing a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear. Sometimes, the fluid itself can become infected, making the symptoms worse and affecting the Eustachian tube's ability to balance ear pressure. If left untreated, middle ear infections can lead to more serious issues, such as hearing loss or ongoing infections.
If you think you may have a middle ear infection, it's important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Other causes
In addition to earwax buildup and Eustachian tube dysfunction, several other factors can cause blocked ears, such as foreign objects and improper ear cleaning.
Foreign objects in the ear:
Small items like beads, cotton swabs, or even insects can sometimes get stuck in the ear canal. This can lead to pain, discomfort, or hearing loss if not removed properly. Never insert anything into your ear canal. If something gets stuck, get medical help to have it safely removed.
Impacted earwax due to improper cleaning methods:
While earwax is important for protecting the ear canal, improper cleaning can push it deeper into the ear, causing a blockage. Using cotton swabs, for example, can push earwax further in and make it harder to remove, leading to discomfort or muffled hearing.
If you think you have impacted earwax, avoid trying to remove it yourself. Instead, see a healthcare professional for safe earwax removal.
Blocked ears symptoms
When your ears are blocked, you may experience a range of symptoms that can affect your hearing and overall comfort. These symptoms can vary in intensity, depending on the cause of the blockage, but they often lead to discomfort and difficulty in daily activities.
Auditory symptoms
Blocked ears often cause noticeable changes in hearing. Here are some common auditory symptoms:
• Muffled hearing or hearing loss: sounds may seem distant, unclear, or distorted, making conversations harder to follow. You might struggle to hear the television or music at normal volumes. In more severe cases, temporary or partial hearing loss can occur, especially if the blockage is caused by earwax buildup, fluid retention, or an ear infection.
• Sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear: many people describe a "stuffed" or clogged feeling in their ear, similar to the sensation experienced when flying or driving through high altitudes. This pressure is often due to fluid buildup, Eustachian tube dysfunction, or earwax blockage. It may feel worse when swallowing, yawning, or changing elevations.

Physical discomfort
In addition to hearing issues, blocked ears can cause physical discomfort.
Ear pain or aching: a blocked ear can sometimes lead to mild discomfort or even sharp, throbbing pain. This can result from earwax buildup, an ear infection, or pressure changes within the middle ear. If the pain is persistent or severe, it may indicate an infection that needs medical attention.
Itchiness or dizziness: some people experience an itchy sensation inside the ear canal, which can be caused by irritation from earwax buildup, allergies, or infections. In some cases, a blocked ear can also affect balance, leading to dizziness or a sensation of being off-balance.
Ringing in the ears (tinnitus): tinnitus often described as ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears, can occur when the ears are blocked. It may be temporary, but if it persists, it could be linked to an underlying issue like an infection, fluid buildup, or prolonged exposure to loud noises.
Diagnosis and when to get medical attention for blocked ears
Blocked ears can be frustrating, but knowing when to get medical help is important for your ear health. Understanding your symptoms and how doctors diagnose ear blockages can help you take the right steps toward relief.
Self-assessment
If your ears feel blocked, start by assessing your symptoms. Ask yourself the following:
• How long has it lasted: if your ears have been blocked for more than a few days and home remedies (like swallowing, yawning, or using over-the-counter ear drops) haven't helped, it may be time to see a doctor.
• How severe is it: if the blockage is causing significant discomfort, pain, or interfering with daily activities, professional evaluation may be necessary.
• Are there other symptoms: if you also have a fever, ear drainage, or noticeable hearing loss, these could be signs of an infection or another condition requiring medical attention.
Professional diagnosis
If home remedies don’t provide relief, a healthcare professional can perform a thorough evaluation using the following methods:
• Ear examination: your healthcare professional may use an otoscope (a special lighted tool) to check for earwax buildup, infections, or other blockages in the ear canal.
• Hearing tests: if hearing loss is a concern, tests like audiometry or tympanometry may be performed to measure how well your ear is functioning.
• Tympanic membrane assessment: the healthcare professional may also check the eardrum for signs of fluid buildup or infection, which could indicate a middle ear infection (otitis media).
When to consult a doctor
You should seek medical help if you experience any of the following:
• Persistent symptoms: if your blocked ears, discomfort, or muffled hearing continue even after self-care methods, it's time to consult a doctor.
• Severe pain, dizziness, or hearing loss: if you experience sharp pain, significant hearing loss, or severe dizziness-especially with fever or ear drainage-seek medical help immediately. These symptoms could indicate an infection or a more serious issue that requires treatment.
How to treat blocked ears
Blocked ears can often be treated at home, but persistent or severe cases may require medical attention. Below are different methods to help relieve ear blockages.
Home remedies
Ear drops for blocked ears
If your blocked ears are caused by earwax buildup, ear drops can help soften the wax, making it easier to remove naturally.
• Over-the-counter ear drops: these are specially designed to break down earwax. Follow the instructions on the packaging and use them for a few days before cleaning your ear.
• Natural alternatives: warm olive oil or hydrogen peroxide can also help loosen stubborn earwax. Just add a few drops into your ear and let it sit for a few minutes before draining.
Techniques to clear eustachian tube blockage
If your blocked ears are due to Eustachian tube dysfunction (caused by colds, allergies, or sinus issues), try these simple techniques:
• Yawning, swallowing, or chewing gum: these actions encourage the Eustachian tube to open, allowing air to flow and equalise ear pressure.
• Valsalva maneuver: gently pinch your nose shut, take a deep breath, and gently blow out through your nose. Be careful not to blow too hard to avoid damaging your ears.
Steam inhalation and warm compresses
For ear blockages caused by congestion, steam and warmth can provide relief:
• Steam inhalation: breathing in steam from a hot shower or a bowl of warm water can help clear nasal congestion, improving airflow and reducing ear pressure.
• Warm compresses: applying a warm cloth to the affected ear can ease discomfort and promote drainage.
Over-the-counter medications
If your ear blockage is due to congestion from a cold, allergies, or sinus issues, certain medications can help:
Best decongestant for blocked ears
Decongestants reduce swelling in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, helping relieve ear pressure.
Use nasal sprays only for short periods (3 days max), as overuse can worsen congestion. If you have high blood pressure or other health conditions, consult your doctor before using decongestants.
Antihistamines
If allergies are causing your blocked ears, antihistamines can help by reducing inflammation and improving airflow. These are especially useful for blockages caused by pollen, dust, or pet dander.
Professional medical treatments
If home treatments don't work, a healthcare provider may recommend one of the following medical procedures:
Ear irrigation
A healthcare professional may flush out excess earwax using a gentle stream of water or saline solution. This method is safe when performed by a professional and is recommended for cases where ear drops haven't been effective.
Manual removal
If earwax is deeply impacted, a doctor may use special tools, like a curette or suction device, to remove it safely.
Surgery
For people with severe, long-term Eustachian tube dysfunction, minor surgical procedures may be needed. These can include:
• Tympanostomy tubes: small tubes inserted into the eardrum to help drain fluid and equalise pressure.
• Balloon eustachian tube dilation: a procedure where a small balloon is inserted and inflated to open the Eustachian tube.
Surgery is usually only considered for persistent, severe cases. Your doctor will evaluate the risks and benefits before recommending it.
How to prevent blocked ears
Preventing blocked ears is simple with a few healthy habits. By maintaining good ear hygiene, managing allergies, and taking precautions during altitude changes, you can reduce the risk of discomfort and blockages.
Proper ear hygiene
Good ear hygiene helps prevent earwax buildup, one of the most common causes of blocked ears.
• Avoid inserting objects into your ears: never use cotton swabs, hairpins, or your fingers to clean inside your ears. These can push earwax deeper, cause irritation, and even lead to injury.
• Use safe cleaning methods: instead of inserting anything into your ear canal, wipe the outer part of your ear with a damp cloth. If you have excessive earwax, consider using over-the-counter ear drops or consult a healthcare provider for safe removal.

Managing allergies and sinus issues
Allergies and sinus problems can lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction, causing blocked ears. Here's how to manage them:
• Control allergies: if you suffer from seasonal allergies, take antihistamines or decongestants as directed by your doctor. These medications reduce inflammation in the Eustachian tube and help prevent mucus buildup.
• Keep your sinuses clear: use a saline nasal spray or neti pot to flush out mucus and prevent pressure buildup in your ears. Managing sinus infections and congestion can also help keep your ears clear.

Protecting ears during altitude changes
Flying, diving, or driving through high-altitude areas can cause ear blockages due to rapid pressure changes.
• Equalise ear pressure: awning, swallowing, or chewing gum can help open the Eustachian tube and balance pressure in your ears.
• Stay hydrated: drinking water keeps the Eustachian tube functioning properly and reduces the risk of ear blockages.
• Use decongestants if needed: if you're prone to ear discomfort during altitude changes, an over-the-counter nasal spray or decongestant can help reduce ear pressure. Be sure to use them as directed to avoid overuse.
Blocked ears can be uncomfortable, but with simple preventive measures, you can keep them clear. Practicing good ear hygiene, managing allergies, and taking precautions during altitude changes can all help reduce the risk.

If you experience persistent ear pain, severe discomfort, or hearing loss, get medical advice. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can ensure your ears stay healthy.



