Everything you need to know about hearing aids for tinnitus

Everything you need to know about hearing aids for tinnitus
7 minutes
Published 15 June 2023
Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears without an external source, and it affects millions of people worldwide. This auditory condition can range from mildly annoying to severely debilitating, impacting your quality of life and mental well-being.
Hearing aids are essential tools in managing tinnitus, amplifying external sounds to mask internal noises. This improves overall hearing and reduces the strain on the brain, easing tinnitus symptoms effectively.
In this article, we'll delve into the world of hearing aids for tinnitus, exploring everything from how they can provide relief to the different types available.
Understanding tinnitus and its impact
Tinnitus can present as ringing, buzzing, humming, or even roaring sounds, varying in pitch and intensity. While not a disease itself, tinnitus often signals an underlying condition such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system disorders.
Causes of tinnitus
Tinnitus can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Age-related hearing loss: as people age, hearing sensitivity tends to decline, which can trigger tinnitus.
Exposure to loud noises: repeated exposure to loud sounds, such as those from heavy machinery, concerts, or headphones, can damage the inner ear.
Ear infections or blockages: infections or blockages in the ear canal can alter the pressure in the ear and lead to tinnitus.
Medications: certain medications, particularly in high doses, can cause or worsen tinnitus.
Impact on individuals
Tinnitus can significantly affect an individual's quality of life. Common symptoms include:
• Persistent ringing, buzzing, or humming noises
• Difficulty concentrating or sleeping
• Increased stress or anxiety
• Problems with hearing external sounds clearly
Prevalence of tinnitus
Approximately 13% of UK adults experience tinnitus, with about 1 in 10 managing persistent symptoms. Nearly 30% of those affected by tinnitus experience constant symptoms, with 20% also battling insomnia, exacerbating their condition.
Understanding the nature of tinnitus and its impact is vital for effective management. Get professional help if you begin experiencing symptoms.
Do hearing aids help with tinnitus?
Hearing aids play a crucial role in alleviating tinnitus symptoms by amplifying external sounds, which masks internal noises like ringing, buzzing, or humming. This process, known as sound therapy, provides relief for many tinnitus sufferers by enhancing auditory input to the brain.
How hearing aids alleviate tinnitus symptoms
Amplification of external sounds: hearing aids boost ambient sounds, helping to overshadow internal tinnitus noises. This makes external sounds more prominent, redirecting the brain's focus away from tinnitus sounds.
White noise generation: some hearing aids feature white noise generators or tinnitus masking features. These emit constant, soothing sounds that help mask tinnitus, reducing its noticeable impact.
Auditory stimulation: increasing auditory stimulation, hearing aids can minimise the perception of tinnitus. They create a richer sound environment that encourages the brain's auditory system to prioritise external sounds over internal ones.
Mechanisms behind hearing aid effectiveness
Neural rewiring: regular use of hearing aids can rewire neural pathways in the brain, diminishing the prominence of tinnitus. Consistent auditory input prompts the brain to adapt, decreasing the perceived intensity of tinnitus.
Stress reduction: tinnitus often induces stress and anxiety, exacerbating symptoms. Hearing aids alleviate this burden by improving hearing and reducing tinnitus-related stress levels, providing additional relief.
Improved communication: hearing aids enhance overall hearing ability, facilitating easier engagement in conversations and daily activities. This improvement enhances quality of life and reduces the social isolation commonly linked with tinnitus.
Types of hearing aids for tinnitus
When it comes to managing tinnitus, several types of hearing aids are specifically designed to provide relief through advanced features.
Here’s a breakdown of the different types and the key features that make them effective for tinnitus relief.
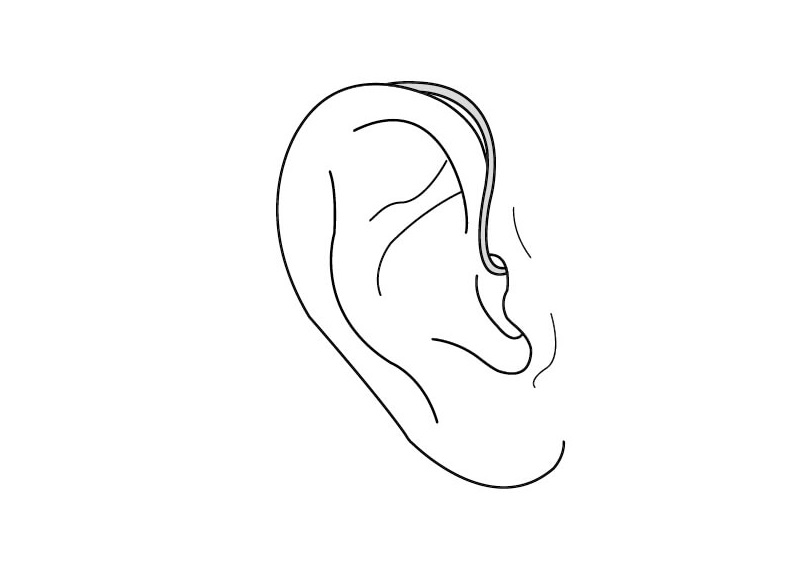
Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids
BTE hearing aids sit comfortably behind the ear and are connected to an ear mould that fits inside the outer ear. These devices are suitable for a wide range of hearing losses and come equipped with several tinnitus management features:
Sound therapy features: BTE hearing aids can be programmed to deliver sound therapy, playing soothing sounds to help mask tinnitus.
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids
ITE hearing aids fit completely inside the outer ear and are custom-moulded to the shape of the user’s ear. They offer a discreet appearance and are suitable for mild to severe hearing loss
Custom sound profiles: ITE hearing aids can be tailored to the specific needs of the user, including custom sound profiles that help manage tinnitus.
Receiver-in-canal (RIC) hearing aids
RIC hearing aids have a small casing behind the ear, with a thin wire connecting to a receiver placed in the ear canal. This design provides a comfortable fit and high sound quality
Versatile sound therapy: RIC hearing aids offer versatile sound therapy features that can be adjusted to suit individual tinnitus needs.
Noise masking: many RIC models include noise-masking features that generate specific sounds to reduce the perception of tinnitus.

Completely-in-canal (CIC) and invisible-in-canal (IIC) hearing aids
CIC and IIC hearing aids are the smallest types available, fitting deeply into the ear canal for a nearly invisible appearance. They are suitable for mild to moderate hearing loss.
Discreet tinnitus relief: despite their small size, these hearing aids can include tinnitus masking features, providing discreet relief.
Customised sound settings: users can benefit from customised sound settings that help subtly manage tinnitus.
Benefits of using a hearing aids for tinnitus
Using hearing aids for managing tinnitus offers a range of long-term benefits that significantly improve the quality of life for individuals experiencing tinnitus. Here are some key advantages:
1. Sound amplification and noise masking
Hearing aids amplify external sounds, helping to mask internal tinnitus noises and redirect focus away from them. Many modern hearing aids also feature noise masking, such as white noise or nature sounds, which further cover tinnitus, providing relief and making the ringing or buzzing less noticeable.
2. Enhanced communication
Improved hearing through hearing aids enhances communication abilities. Clearer perception of conversations and important sounds in various environments enables better social interactions and engagement in daily activities. This is crucial for maintaining relationships and feeling connected to surroundings.
3. Improvement in quality of life
The combined effect of sound amplification, noise masking, and improved communication significantly enhances overall quality of life for tinnitus sufferers. By reducing the prominence of tinnitus symptoms and facilitating better hearing, individuals can enjoy a more active lifestyle, improved emotional well-being, and reduced stress associated with tinnitus.
4. Customisable solutions
Modern hearing aids offer customisable solutions tailored to individual tinnitus needs. This includes personalised sound therapy programs, adjustable settings for different environments, and integration of additional tinnitus management techniques. Customisation ensures users receive optimal relief and comfort specific to their tinnitus symptoms.
Choosing the right hearing aid for tinnitus
Selecting the right hearing aid for managing tinnitus involves considering several key factors to ensure optimal relief and functionality.
Here's a guide to help you make an informed decision:
Factors to consider
Degree of hearing loss: understanding the extent of your hearing loss is crucial. Hearing aids are available in different models and strengths to accommodate mild to profound hearing loss. Your audiologist will conduct comprehensive tests to determine the appropriate level of amplification needed for both hearing improvement and tinnitus management.
Type and severity of tinnitus: tinnitus varies in type and severity among individuals. Some experience ringing, buzzing, or pulsing sounds. Certain hearing aids are designed with features like sound therapy or tinnitus maskers to effectively alleviate these symptoms. Discussing your tinnitus characteristics with your audiologist helps find a suitable solution.
Lifestyle considerations: consider your daily activities and environments. If you lead an active lifestyle or frequent noisy settings, hearing aids with advanced noise reduction capabilities may benefit you. Alternatively, smaller, less visible hearing aid models are available for those preferring discreet options.
Budget: hearing aids vary in cost based on technology and features. While budget is important, weigh long-term benefits of effective tinnitus management and improved hearing quality against initial expenses.
Importance of audiologist consultation
Consulting with an audiologist is crucial for personalised care and optimal outcomes when selecting a hearing aid for tinnitus:
Personalised fitting: an audiologist performs detailed assessments, including hearing tests and tinnitus evaluations. Based on results, they recommend hearing aids tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
Adjustments and follow-up: after picking a hearing aid, the audiologist ensures proper fitting and adjusts settings to optimise performance. Regular follow-up appointments monitor progress, make adjustments, and address concerns.
Overview of the process
Other ways to manage tinnitus
While hearing aids are effective for managing tinnitus, there are other approaches individuals can consider:
Environmental adjustments: managing volume levels on electronic devices and keeping a safe distance from loud noises can reduce tinnitus aggravation. Using earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments also helps protect hearing.
Therapeutic support: seeking therapy or medical consultation can aid in diagnosing underlying conditions contributing to tinnitus. Therapists or doctors can provide strategies to cope with tinnitus-related stress and anxiety.
Earwax management: sometimes, excessive earwax can exacerbate tinnitus. Removing earwax through professional earwax removal services can alleviate symptoms.
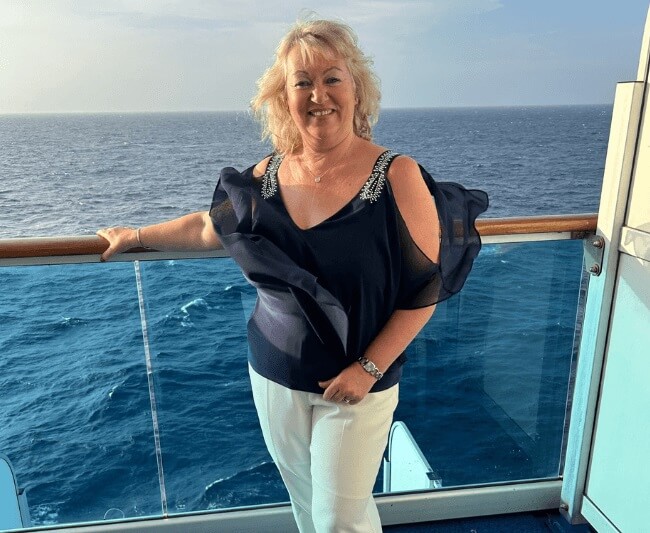
Case study: how hearing aids helped my tinnitus
Meet Mel
Mel runs a busy estate agency with her husband and enjoys an active lifestyle. After living with untreated hearing loss and tinnitus for 15 years, Mel sought help at Boots Hearingcare. "I brushed it off in the beginning, but my hearing got progressively worse – I couldn’t hear anyone," Mel shared. Inspired by Kaye Adams' journey on Loose Women, Mel opted for Phonak hearing aids at Boots Hearingcare. They provided relief, improving her ability to hear conversations in noisy places and enjoy family events like weddings".

Frequently asked questions
Author
Boots Hearingcare
Boots Hearingcare



