Perforated eardrum: Symptoms, causes, and treatment
.jpg?branch=web_prod)
Perforated eardrum: Symptoms, causes, and treatment
4 minutes
Published 18 June 2024
15 January 2025
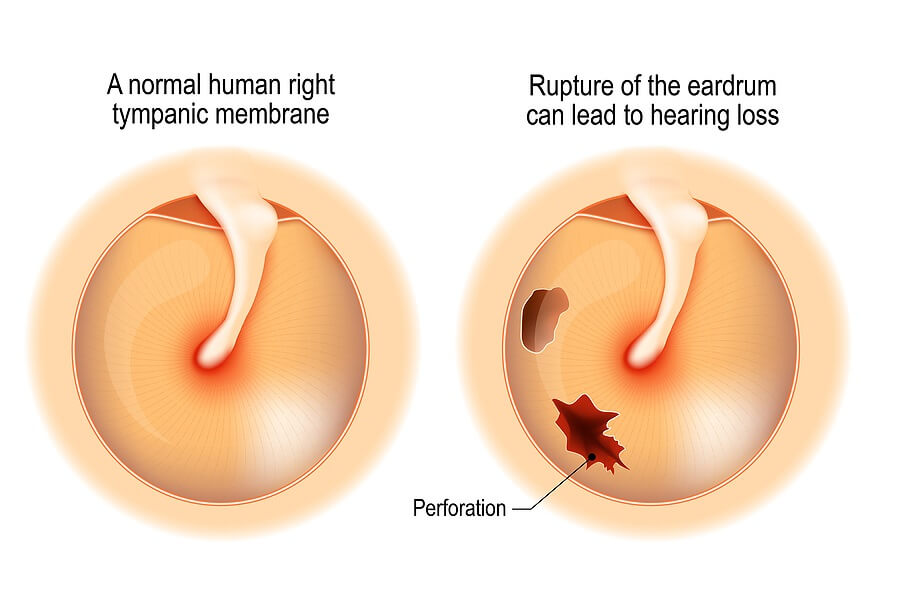
A perforated eardrum, also known as a ruptured eardrum, occurs when the thin membrane that separates the ear canal from the middle ear tears. This condition can cause hearing loss, ear pain, and sometimes fluid discharge, which can affect daily activities such as conversations and listening to music. It also raises the risk of ear infections. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment is essential for managing symptoms and preventing further problems.
What is a perforated eardrum?
A perforated eardrumoccurs when the thin tissue deep in the ear canal ruptures, resulting in ear pain and temporary hearing loss.
This delicate layer serves to shield the vulnerable middle and inner ear from external factors. Getting immediate medical advice is crucial to assess potential damage and infection. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the ruptured membrane.
At Boots Hearingcare, we delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatments for a perforated eardrum, emphasising our commitment to comprehensive ear health awareness.
Does a perforated eardrum hurt?
A perforated eardrum can cause different levels of pain and discomfort. For some, it's a sharp, intense pain, whilst for others, it may feel more like a dull ache. Pain intensity varies widely among individuals, and some may not feel any pain at all.
What causes a perforated eardrum?
A perforated eardrum,can occur due to several factors:
Infections: middle ear infections (otitis media) are a common cause. These infections can build up pressure behind the eardrum, leading to it rupturing. Severe infections, such as chronic otitis media or acute otitis media with pus buildup, can exert enough pressure to perforate the eardrum.
Trauma: direct trauma to the ear, such as a blow to the ear, inserting objects into the ear canal (like cotton swabs), or exposure to loud blasts or explosions, can cause the eardrum to tear.
Pressure changes: rapid changes in air pressure, such as during air travel, scuba diving, or sudden explosions, can create a pressure difference between the middle ear and outer ear. This imbalance in pressure can rupture the eardrum.
Any of these causes can lead to a perforated eardrum. Getting medical attention as soon as possible is essential to prevent complications and support the healing process.
Perforated eardrum symptoms
The most common sign of a perforated eardrum is pain or fullness in the ear; however, you can also rupture your eardrum without knowing it.
Other indications of a burst eardrum include:
Symptoms normally pass as soon as the eardrum is healed, and any infection has cleared up. Contact your doctor if this fails to happen, or if the condition appears to be worsening.
Perforated eardrum treatment
Any tear or hole in your eardrum should be addressed promptly. Effective management of a perforated or burst eardrum involves several key steps:
Diagnosis
The first step in treating a perforated eardrum is diagnosis. Your GP will use a magnifying instrument called an otoscope to examine the ear and identify any tears or holes in the eardrum. They may also assess your overall hearing ability to understand the extent of the rupture and its possible causes.
Treatment
Perforated eardrums often heal on their own within a few weeks, so immediate treatment may not always be necessary. However, consulting your GP is crucial to determine the underlying cause and assess whether any treatment is needed.
Medication
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat an existing ear infection or prevent one from developing. Over-the-counter pain relievers and warm compresses applied to the affected ear can also help alleviate discomfort as the eardrum heals.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of a perforated eardrum, avoid activities that could introduce bacteria into the ear, such as swimming or getting water in your ears. Refrain from inserting objects like cotton buds into your ears, as this can damage the eardrum. If something gets lodged in your ear, get medical assistance instead of attempting to remove it yourself.
Perforated eardrum surgery
Most perforated eardrums heal naturally within a few weeks. However, if there is no improvement or if the perforation is large, your doctor may recommend a surgical procedure called myringoplasty to repair the eardrum.
Prevention tips
Frequently asked questions
Author
Boots Hearingcare
Boots Hearingcare



