conditions
conditions
Boots Hearingcare
Feb 26, 2021
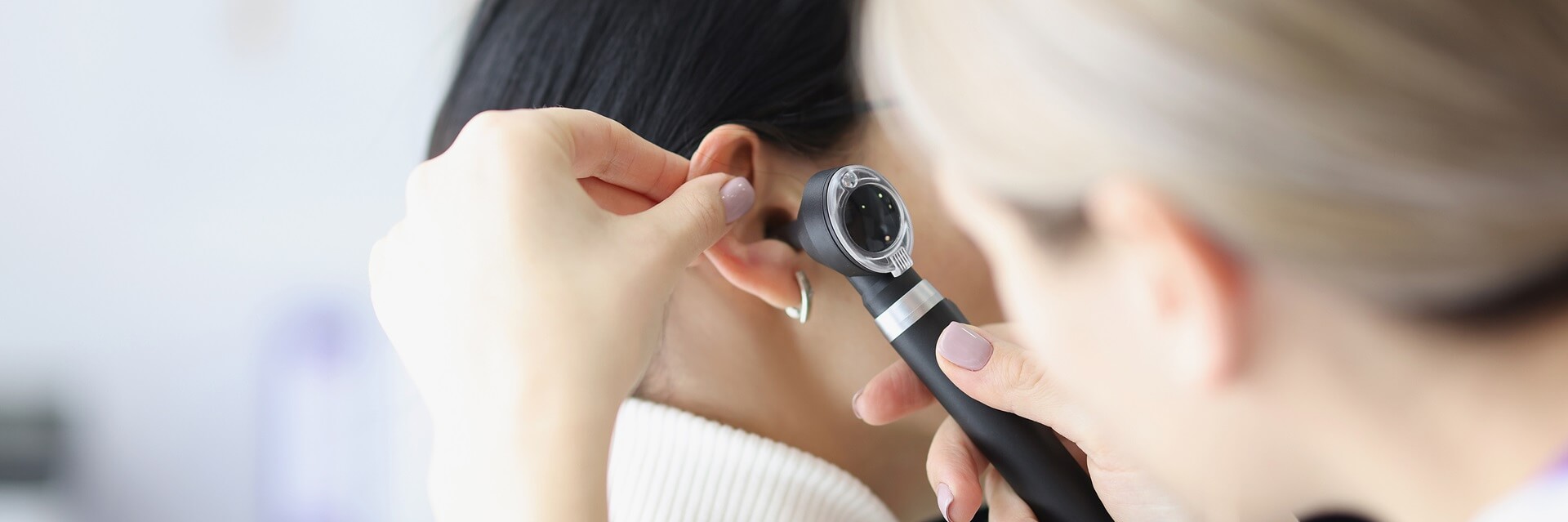
Bilateral hearing loss: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Bilateral hearing loss, or BHL, refers to the permanent loss of hearing in both ears. Caused by several factors, bilateral hearing loss can be categorised due to the degree of hearing loss. The condition normally occurs as a result of damage to stereocilia - hair-like cells in the inner ear - or to the auditory nerve itself.